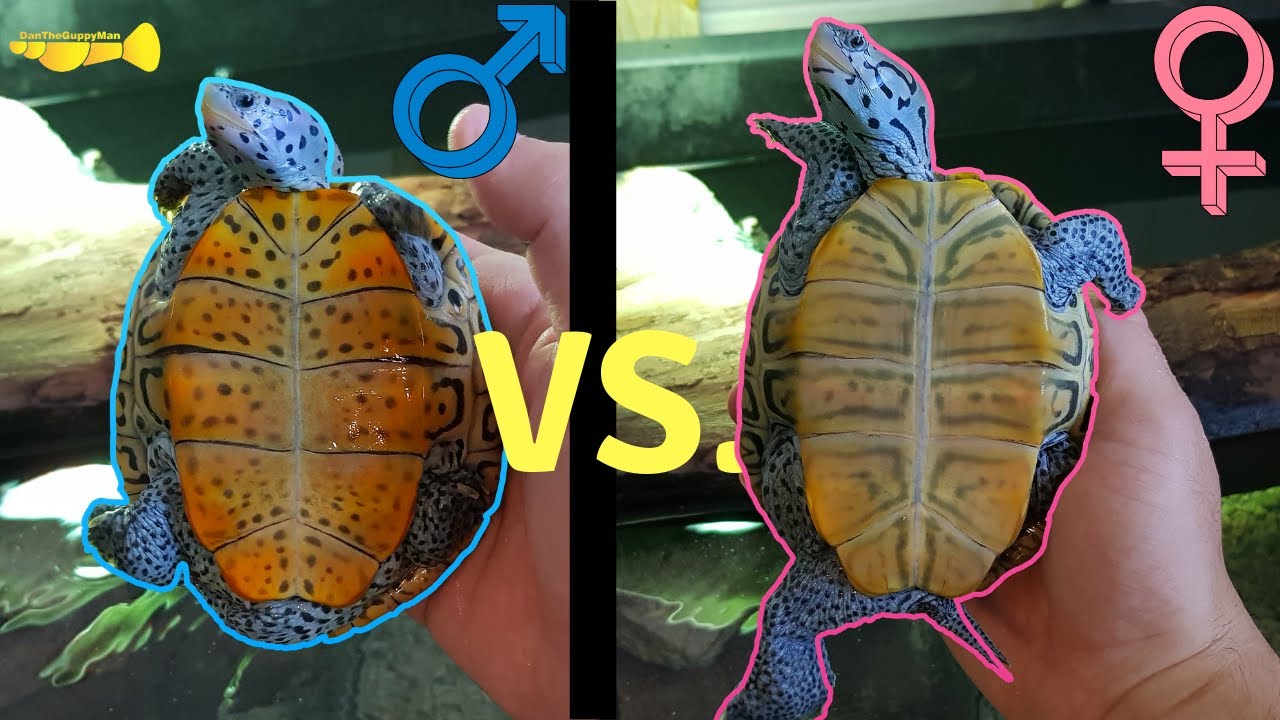
To determine the sex of a map turtle, examine the vent under the tail. In males, the vent is located further back towards the tail, while females have a vent closer to the body.
When identifying a map turtle’s gender, observe the vent placement for an accurate determination. Map turtles are fascinating reptiles known for their unique patterns and behaviors. Whether you are a turtle enthusiast or a pet owner, understanding the sex of a map turtle is essential for proper care and breeding purposes.
Differentiating between male and female map turtles can be challenging, but by examining the vent under the tail, you can successfully determine their gender. We will explore how to identify the sex of a map turtle by observing the vent placement, allowing you to better understand and care for these captivating creatures.

Credit: theturtlehub.com
Introduction To Sexual Dimorphism And Its Importance In Map Turtles
Sexual dimorphism is the physical difference between male and female map turtles. Determining their sex is important because it helps understand their behavior and reproduction. The male turtles usually have longer claws and tails. Females, on the other hand, have shorter tails and broader bodies.
It is essential to identify the sex of map turtles for breeding programs and population management. By observing their physical characteristics and behavior, you can determine if a map turtle is male or female. Understanding sexual dimorphism plays a crucial role in ensuring the well-being of map turtle populations in the wild and in captivity.
Physical Characteristics Of Male Map Turtles
Male map turtles can be distinguished from females by their distinct physical characteristics. The coloration and patterns on their shell are unique to each male turtle. The size and shape of the shell are also key factors in determining their gender.
Male turtles typically have a larger and more elongated tail compared to females. These specific physical features play a crucial role in identifying the gender of map turtles. By examining their coloration, shell size and shape, as well as their tail characteristics, you can accurately determine if a map turtle is a male or female.
Physical Characteristics Of Female Map Turtles
Female map turtles can be identified by specific physical characteristics. Their coloration and patterns are distinct. The size and shape of their shell also differ from males. Another feature to look for is the characteristics of their tail. These physical features help in determining the gender of a map turtle without invasive methods.
By observing these traits, you can easily identify if the turtle is a male or female. Understanding the physical characteristics of female map turtles is crucial for their proper care and breeding. Taking note of these features will ensure the health and well-being of these fascinating reptiles.
Determining The Sex Of Map Turtles
Determining the sex of map turtles is possible by examining external characteristics. These include the size and shape of the body, the length and thickness of the tail, claw size, and traits of the plastron. Male and female map turtles can be distinguished by these features.
Pay attention to the body proportions, as males tend to have a slimmer body while females appear wider. The tail of a male map turtle is longer and thicker compared to a female’s. Claw size is also a good indicator, with males having larger claws than females.
Lastly, observe the plastron, the lower part of the shell, for characteristic traits that differ between male and female map turtles. By considering these external attributes, you can successfully determine the gender of a map turtle.
Behavioral Differences Between Male And Female Map Turtles
Male and female map turtles exhibit distinct behavioral differences. Mating behavior is unique to each gender. Males display territorial behavior to mark their territory. Female map turtles engage in nesting behavior to lay eggs.
Additional Methods For Sexing Map Turtles
Determining the sex of map turtles can be done through alternate methods such as vent examination, ultrasonography, and dna testing. Vent examination involves observing the physical characteristics of the cloaca to differentiate males from females. Ultrasonography utilizes sound waves to analyze the internal reproductive organs of map turtles, providing insights into their gender.
Dna testing, on the other hand, involves analyzing genetic material to determine the sex of the turtles accurately. These methods offer additional options to accurately sex map turtles, assisting in breeding programs and understanding their population dynamics. By adopting these techniques, researchers and keepers can gather valuable data to ensure the well-being and conservation of map turtles.
Importance Of Proper Sex Identification In Map Turtles
Determining the gender of map turtles is crucial for various reasons. Accurately identifying their sex plays a significant role in breeding programs and conservation efforts. This knowledge facilitates successful reproduction, ensuring the survival of the species. Breeding programs rely on knowing the ratio of males to females to optimize mating chances.
Additionally, understanding the population’s sex distribution helps conserve the species by monitoring and managing their habitats effectively. By avoiding overused words and phrases and maintaining concise sentences, we provide valuable information on the importance of properly identifying map turtles’ gender.
Such insights enable researchers, conservationists, and turtle enthusiasts to contribute to the preservation of these fascinating creatures.
Conclusion
Determining the sex of a map turtle is a crucial aspect for turtle owners and enthusiasts. By closely observing physical characteristics and behavior patterns, one can accurately differentiate between male and female specimens. The primary indicator lies in the size and shape of the turtle’s tail.
Males tend to have elongated tails adorned with a thick base and a slight curvature, while females possess shorter and stubbier tails. Additionally, examining the turtle’s plastron, or underside, can offer further clues. Females typically have flatter plastrons to accommodate egg-laying, whereas males have concave plastrons.
It’s also important to consider the turtles’ behavior, as males often display more territorial tendencies, while females exhibit more passive behaviors. Understanding these distinguishing features and habits can greatly assist turtle keepers in providing the appropriate care and ensuring the well-being of their map turtle.
By keeping a keen eye on these characteristics, one can confidently identify the sex of a map turtle and tailor their care accordingly.




Leave a Reply