Yes, turtles are primary consumers. They mainly feed on plants and algae.
Turtles, as primary consumers, play a crucial role in the food chain by consuming plant matter and algae. Their diet consists primarily of vegetation, making them important for regulating plant populations and nutrient cycling in their ecosystems. This dietary preference places them at the bottom of the food chain, where they serve as a link between producers (plants) and higher-level consumers.
As primary consumers, turtles contribute to the balance and sustainability of their habitats, showcasing the significance of their role in the natural world. Understanding the primary consumer status of turtles sheds light on their ecological importance and their impact on the broader ecosystem.
Introduction To Turtles And Their Diets
Turtles, known as primary consumers, mainly feed on plants, insects, and small fish. Their diets consist of a variety of vegetation and protein sources, making them essential for maintaining ecosystem balance and diversity. These fascinating creatures play a crucial role in the food chain as primary consumers.
Turtles are fascinating creatures that belong to the reptile family. They are known for their hard shells, which provide them with excellent protection from predators. Turtles are found in different parts of the world, from the oceans to freshwaters and even on land. They come in various sizes, shapes, and colors, making them a popular pet choice for many people. One of the essential aspects of a turtle’s life is their diet. In this article, we will be discussing the different types of turtles and their dietary habits.
Turtle Species Diversity
There are over 300 species of turtles in the world, and they all have different dietary habits. Sea turtles, for instance, are herbivores, while others like the snapping turtle are carnivores. Some turtles are omnivores, which means they eat both plants and animals. Here are some of the common turtle species and their diets:
| Turtle Species | Diet |
|---|---|
| Green Sea Turtle | Seagrasses and algae |
| Box Turtle | Insects, worms, and fruits |
| Snapping Turtle | Fish, insects, and small mammals |
| Painted Turtle | Plants, insects, and small fish |
General Dietary Habits Of Turtles
Turtles have a diverse diet, and their feeding habits vary depending on their environment and species. As mentioned earlier, some turtles are herbivores, while others are carnivores. However, most turtles are omnivores, which means they eat both plants and animals. Turtles have a slow metabolism, which means they do not need to eat as often as other animals. Some turtles can go for several weeks without food.
Turtles have a unique feeding behavior that involves biting and chewing their food. They have beaks instead of teeth, which they use to bite off pieces of their food. They also have a muscular stomach that allows them to grind and break down their food. Turtles are also known for their ability to store food in their esophagus, which helps them to survive during times of scarcity.
In conclusion, turtles are primary consumers that play an essential role in the ecosystem. Their dietary habits are diverse and vary depending on their species and environment. Understanding a turtle’s diet is crucial for their overall health and wellbeing.

Trophic Levels And Food Chains
Turtles are considered primary consumers in food chains, feeding on plants and small animals. They occupy a lower trophic level, showcasing their role in transferring energy from producers to higher-level consumers in aquatic ecosystems. This highlights their importance in maintaining ecological balance.
The Role Of Primary Consumers
When it comes to understanding trophic levels and food chains, it is important to recognize the role of primary consumers. These organisms occupy the second level in the food chain and play a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems.
Primary consumers, also known as herbivores, are organisms that primarily feed on plants and other producers. They obtain energy and nutrients by consuming these primary producers, such as grass, leaves, or algae. This makes them an essential link between the producers and other levels of the food chain.
In an ecosystem, primary consumers serve as the primary source of food for secondary consumers, which include carnivores and omnivores. Without primary consumers, the energy flow in the food chain would be disrupted, leading to imbalances in the ecosystem.
Understanding The Food Web
To fully grasp the concept of trophic levels and food chains, it is crucial to understand the interconnectedness of organisms in a food web. A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that illustrates the flow of energy and nutrients in an ecosystem.
At the base of the food web, we find the primary producers, such as plants and algae. These organisms convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, making them the primary source of energy for the entire ecosystem. The primary consumers, including herbivores like turtles, then feed on these producers.
As we move up the trophic levels, secondary consumers consume primary consumers, and tertiary consumers feed on secondary consumers. This hierarchy continues until we reach the apex predators, which have no natural predators themselves.
Understanding the food web helps us comprehend the complex relationships between organisms and their dependence on one another for survival. It also highlights the importance of maintaining a balanced ecosystem by ensuring the presence of primary consumers like turtles.
Turtles In Ecosystems
Turtles play an important role in various ecosystems around the world. From freshwater lakes and rivers to coastal habitats, these remarkable creatures contribute to the balance and stability of their environments. In this section, we will explore two key aspects of their ecological significance: their habitats and feeding grounds, and their interactions with other species.
Habitats And Feeding Grounds
Turtles inhabit diverse ecosystems, each with its own unique characteristics. They can be found in various habitats such as wetlands, forests, grasslands, and even deserts. However, turtles are most commonly associated with aquatic environments, including oceans, seas, rivers, and ponds.
When it comes to feeding, turtles display a wide range of dietary preferences. Some species are herbivores, primarily consuming plants and algae, while others are omnivores, eating both plant matter and small invertebrates. There are also carnivorous turtles that rely on a diet of fish, insects, and crustaceans.
It is important to note that turtles act as primary consumers in their ecosystems. As they consume plants and smaller animals, they play a crucial role in regulating populations and maintaining the balance of the food chain. By controlling the abundance of certain species, turtles help prevent overpopulation and protect the overall health of their habitats.
Interactions With Other Species
Turtles interact with a wide range of species within their ecosystems. These interactions can be both beneficial and essential for the overall functioning of the ecosystem. Let’s explore a few examples:
- Turtles and Fish: In aquatic environments, turtles and fish often share the same habitats. While some turtle species may prey on fish, others have a symbiotic relationship with them. Turtles can act as “cleaners” by feeding on parasites and dead skin of fish, helping to keep fish populations healthy.
- Turtles and Birds: In certain ecosystems, turtles create nesting sites that are later used by birds. These nesting sites provide shelter and protection for bird species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
- Turtles and Plants: Turtles play a crucial role in seed dispersal. As they move between different habitats, turtles may unintentionally transport seeds on their bodies or through their digestive systems. This process helps plants spread and colonize new areas.
These are just a few examples of the intricate connections that turtles have with other species in their ecosystems. Their presence and behaviors have a cascading effect on the overall health and stability of the environment.
Dietary Analysis Of Turtles
When it comes to the dietary analysis of turtles, understanding their primary consumers status is essential. Turtles are primarily herbivores, but some species also consume small fish, insects, and carrion, making them omnivorous. Their diet varies based on their species, habitat, and availability of food sources.
Common Foods Consumed By Turtles
Turtles commonly consume aquatic plants, algae, and various forms of vegetation. Some species, like the snapping turtle, also feed on small fish, frogs, and even small mammals. The dietary habits of turtles are diverse, reflecting their adaptability to different environments.
Variations In Turtle Diets
The diet of turtles can vary significantly based on their environment and available resources. For instance, freshwater turtles predominantly consume plant matter, while sea turtles have a diet primarily consisting of jellyfish, seaweed, and algae. This variation in their diets allows turtles to thrive in diverse ecosystems.
Turtles As Primary Consumers
Turtles, fascinating creatures that they are, play an important role in the food chain as primary consumers. As primary consumers, turtles primarily feed on plants and algae, making them an essential link between producers (plants) and the rest of the ecosystem. Let’s explore the different types of turtles and their dietary habits.
Herbivorous Turtles
Herbivorous turtles, as the name suggests, mainly consume plant matter. Their diet consists of various types of vegetation, including aquatic plants, grasses, and leaves. Some common examples of herbivorous turtles include the Green Sea Turtle and the Eastern Box Turtle.
These turtles have specialized beaks or jaws that allow them to efficiently chew and consume plant material. They have flat, broad mouths that help them graze on vegetation and reach algae growing on rocks or submerged surfaces.
Herbivorous turtles are crucial for maintaining the balance of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. They help control the growth of plants, ensuring they do not overtake their surroundings, and provide food for other organisms further up the food chain.
Omnivorous Turtles And Their Plant Diet
Omnivorous turtles, unlike herbivorous turtles, have a more varied diet that includes both plant and animal matter. While they consume plant material, they also feed on small invertebrates, fish, and carrion. However, let’s focus on their plant-based diet.
Omnivorous turtles often eat a combination of fruits, berries, and vegetables along with their primary plant-based diet. They may consume fallen fruits, berries, and even mushrooms that are available in their habitat. These turtles also eat aquatic plants, such as water lilies and duckweed, which are a significant part of their diet.
By consuming plant material, omnivorous turtles contribute to the dispersal of seeds and play a role in the growth and distribution of various plant species. Their diet also aids in nutrient cycling within their ecosystems.
In Conclusion
Turtles, whether herbivorous or omnivorous, fulfill the vital role of primary consumers in the food chain. Their consumption of plants and algae helps maintain the delicate balance of ecosystems, benefiting both the plants and other organisms that rely on them. Understanding the dietary habits of turtles allows us to appreciate their ecological significance and the interconnectedness of all living beings.
Case Studies
Case studies provide valuable insights into the primary consumer status of turtles. By examining specific turtle species and making observations in their natural habitats, researchers have gained a deeper understanding of the role these creatures play in their ecosystems.
Research On Specific Turtle Species
Scientists have conducted extensive research on various turtle species to determine their position in the food web. Studies have revealed that turtles primarily consume plant matter, insects, and small aquatic animals, establishing them as primary consumers.
Observations From Natural Habitats
Direct observations in natural habitats have further confirmed the dietary habits of turtles. These observations have shown that turtles feed on algae, aquatic plants, and invertebrates, solidifying their status as primary consumers within their ecosystems.
Impact Of Turtles On Ecosystems
Turtles play a crucial role in ecosystems, impacting various aspects of their environment. Let’s explore how turtles influence the delicate balance of ecosystems, from being both prey and predator to contributing to the overall ecosystem stability.
Turtles As Prey And Predator
- Turtles are consumed by various predators.
- They also feed on small aquatic organisms.
- Act as prey for birds, mammals, and larger reptiles.
Contribution To Ecosystem Balance
- Turtles help control populations of prey species.
- They maintain the health of aquatic vegetation.
- Contribute to nutrient cycling in aquatic ecosystems.
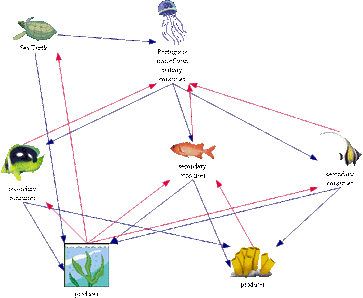
Conservation And The Role Of Turtles
Turtles play a vital role in the ecosystem as primary consumers, feeding on algae, seagrass, and small aquatic creatures. Their conservation is crucial for maintaining the balance of marine and freshwater environments, as they contribute to nutrient cycling and help control populations of their prey.
Threats To Turtle Populations
Turtles face threats like habitat destruction, pollution, and illegal trade.
Importance Of Protecting Turtles
Turtles play a vital role in maintaining ecosystem balance.
Conserving turtles helps sustain biodiversity and a healthy environment.

Frequently Asked Questions
Are Turtles Primary Consumers?
Turtles are not primary consumers; they are usually considered secondary consumers. They primarily consume plants, algae, and small insects, contributing to the ecosystem’s balance by controlling populations of their prey.
Do Turtles Play A Vital Role In The Food Chain?
Yes, turtles play a crucial role in the food chain. As primary or secondary consumers, they help maintain the ecosystem’s balance by controlling populations of plants and animals lower in the food chain.
How Do Turtles Contribute To The Environment?
Turtles contribute to the environment by maintaining the balance of various species populations. They help control vegetation growth by consuming plants and algae, and they provide food for predators higher up in the food chain.
What Impact Do Turtles Have On Their Habitats?
Turtles have a significant impact on their habitats by influencing the populations of the species they consume. Their feeding habits help regulate plant growth, insect populations, and maintain the balance of the ecosystem they inhabit.
Conclusion
After exploring the topic of whether turtles are primary consumers, we can conclude that they are indeed primary consumers. As herbivores, turtles consume a variety of plant matter, making them an essential part of the food chain. However, it’s important to note that turtles also have predators and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystem.
Understanding the role of turtles in the food chain is vital for their conservation and the health of our planet.





Leave a Reply